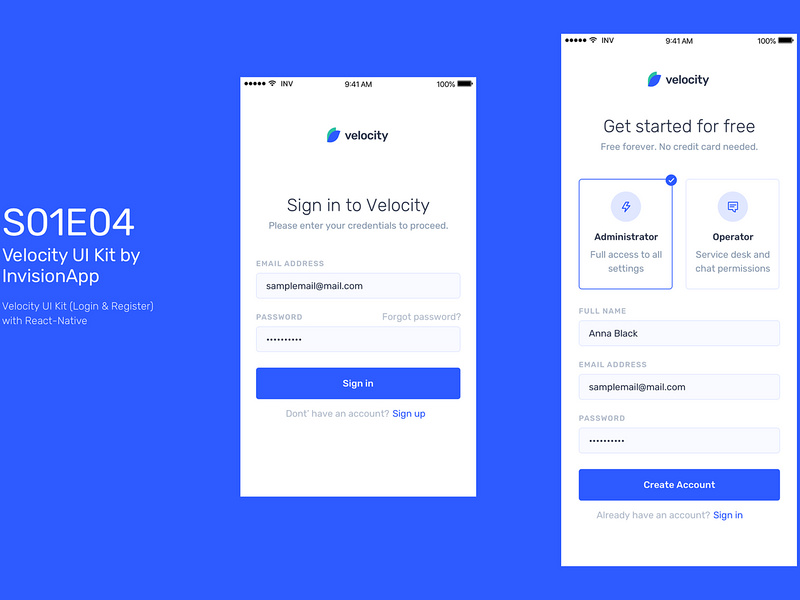
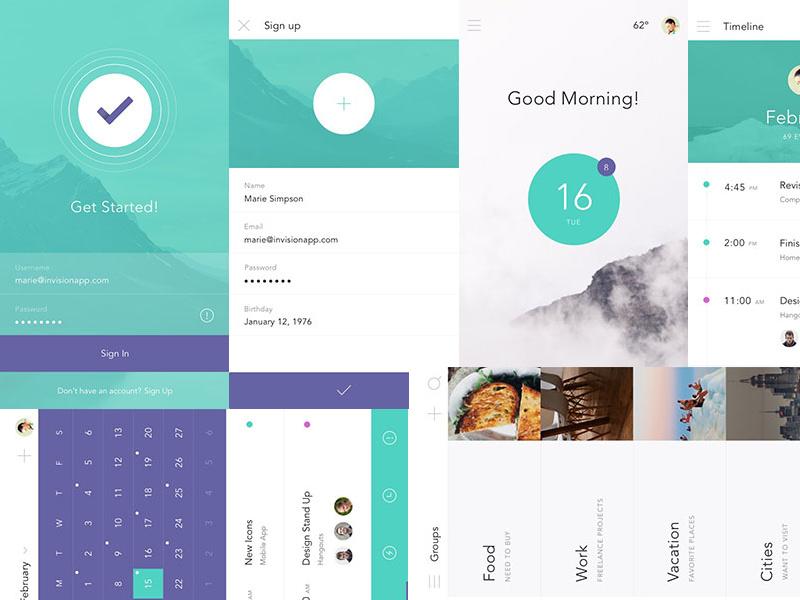
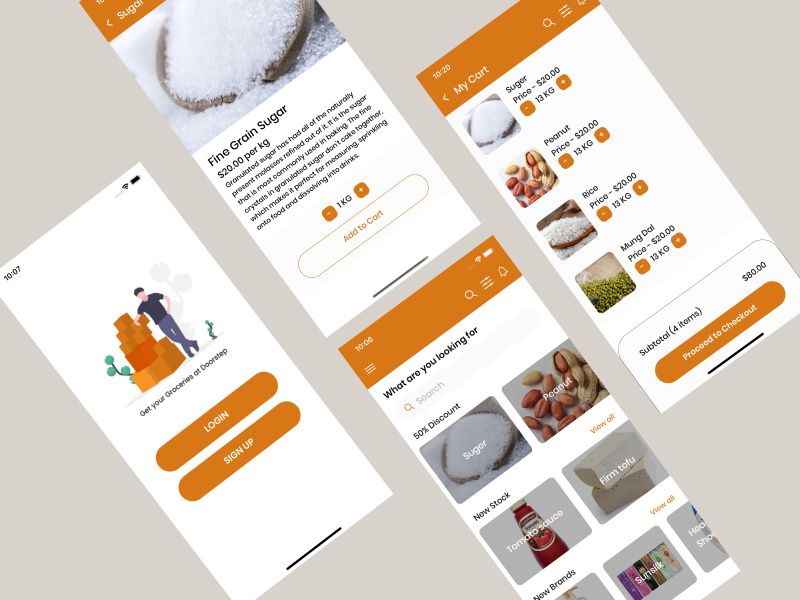
React Native useful resources
Cool react native resources that can help you create interesting products


React Native useful resources
With React Native, you don't build a "mobile web app", an "HTML5 app", or a "hybrid app". You build a real mobile app that's indistinguishable from an app built using Objective-C or Java. React Native uses the same fundamental UI building blocks as regular iOS and Android apps. You just put those building blocks together using JavaScript and React.
React Native components are pure, side-effect-free functions that return what the views look like at any point in time. For this reason it is easier to write state-dependent views, as you don’t have to care about updating the view when the state changes since the framework does this for you.
React Native commenced as Facebook’s hackathon project developed in response to the company’s needs. Facebook wanted to bring all the advantages of web development – such as quick iterations and having a single team develop the whole product – to mobile. That is how React Native was brought to life and leveraged in mobile app development for both iOS and Android apps.
Originally, Facebook only developed React Native to support iOS. However, with it’s recent support of the Android operating system, the library can now provide mobile UIs for both platforms. Facebook used React Native to develop its own Ads Manager app, creating both an iOS and an Android version. Both versions were created by the same team of developers. Facebook also made React Native open-source, with the idea that compatibility with other platforms like Windows or tvOS could be operated on by the development community, so stay tuned.
The social networking platform isn’t the only React Native application that was developed under Facebook’s roof. Facebook Ads was actually the first React Native app for Android and, the first fully React Native based, cross-platform app built in the company. The framework seemed perfectly suitable for the lot of complex business logic required to accurately handle differences in ad formats, time zones, date formats, currencies, currency conventions, and so on, especially that a big chunk of it was already written in JavaScript. On top of that, implementation of UI surfaces with much data would be much easier with React Native.